Key Facts
- In this topic we discussed about blockchain and their benefits.
- Blockchain help us for to create a decentralize network.
- Some blockchain feature are such as security, transparency, decentralization etc.
Blockchain is a revolutionary decentralized and distributed ledger technology that ensures secure, transparent, and immutable recording of transactions across multiple computers. By eliminating the need for intermediaries, blockchain enables peer-to-peer digital transactions, increases accountability, and reduces the risk of fraud. Its applications span various industries, including cryptocurrencies, supply chain management, healthcare, and finance, making it a powerful tool for enhancing efficiency and security in data management and transactions. Despite challenges like scalability and regulatory uncertainties, blockchain’s potential to transform industries remains significant. Here’s a breakdown of how it works and its key features:
How Blockchain Works
Decentralization: Instead of being stored in a single location, a blockchain’s data is distributed across a network of computers, known as nodes. Each node has a copy of the entire blockchain.
Blocks and Transactions: Data is recorded in blocks, and each block contains a list of transactions. Once a block is filled with transactions, it is added to the chain in a linear, chronological order.
Hashing: Each block contains a unique code called a hash, along with the hash of the previous block. This links blocks together, ensuring the integrity and security of the data.
Consensus Mechanism: Before adding a new block, the network must reach a consensus. This process varies, with common mechanisms including Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).
Immutability: Once data is recorded in a block and added to the chain, it cannot be altered. This ensures that the information remains tamper-proof.

Key Features of Blockchain
Security: Blockchain uses cryptographic techniques to secure data, making it resistant to hacking and fraud.
Transparency: All participants have access to the same data, promoting trust and accountability.
Decentralization: No single entity has control over the entire blockchain, reducing the risk of manipulation.
Efficiency: Transactions can be processed quickly and without the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and delays.

Applications of Blockchain
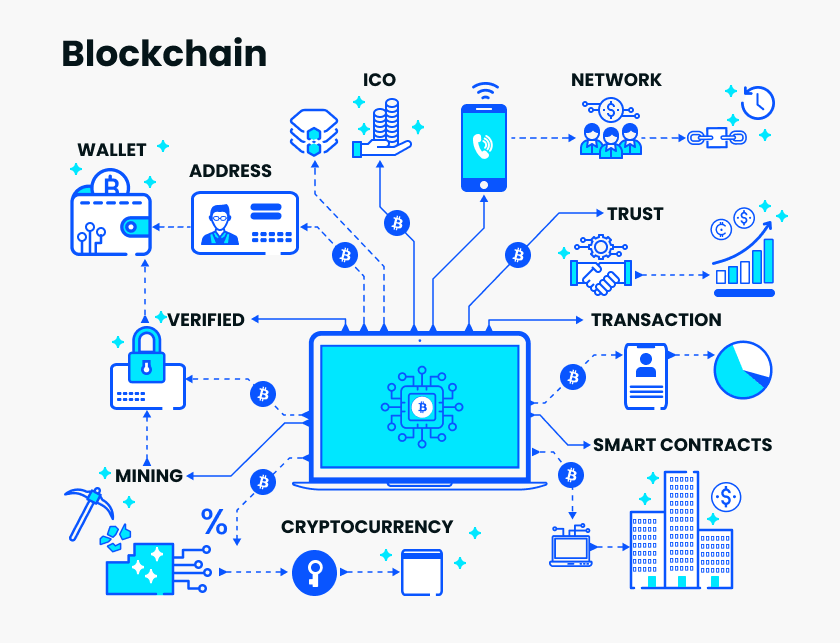
- Cryptocurrencies: The most well-known application, with Bitcoin being the first and most popular cryptocurrency.
- Supply Chain Management: Tracking the journey of goods from origin to consumer to ensure authenticity and transparency.
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code, enabling automated and trustless transactions.
- Healthcare: Securely storing patient records and ensuring they are accessible only to authorized parties.

Advantages of Blockchain:
- Transparency: All transactions are visible to network participants, ensuring accountability and reducing the risk of fraud.
- Security: Cryptographic algorithms and decentralization make blockchain highly secure and resistant to tampering.
- Immutability: Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring data integrity.
- Efficiency: Blockchain can streamline processes, reduce intermediaries, and lower transaction costs.
Challenges of Blockchain:
- Scalability: Handling a large number of transactions simultaneously can be challenging for blockchain networks.
- Energy Consumption: Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanisms, used by some blockchains, require significant computational power and energy.
- Regulatory Issues: The regulatory landscape for blockchain and cryptocurrencies is still evolving, and there are uncertainties regarding legal and compliance aspects.
Blockchain has the potential to revolutionize various industries by providing a secure, transparent, and efficient way to manage data and transactions.
Blockchains are decentralized digital ledgers that record transactions across multiple networks, ensuring transparency, security, and immutability.
— Dianaa💫🤍#WID (@dianaajiboyewa) January 17, 2025
Think of a blockchain as “blocks connected by chains,” where each block holds transaction data that can’t be altered once added. pic.twitter.com/1u9QsOdIAf
Subscribe to our newsletter!